State Management and ways to handle Cache in Web Farm/Web Garden scenario
Basics about State management:
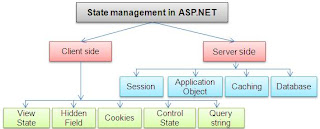
As we all know,web is stateless .A Web page is recreated every time it is posted back to the server.In traditional web programming, that all the information within the page and control gets wiped off on every post back. To overcome this problem,ASP.NET framework provides various ways to preserve the states at various stages like controlstate,viewstate, cookies, session etc.These can be defined in at client side and server side state management.
As we all know,web is stateless .A Web page is recreated every time it is posted back to the server.In traditional web programming, that all the information within the page and control gets wiped off on every post back. To overcome this problem,ASP.NET framework provides various ways to preserve the states at various stages like controlstate,viewstate, cookies, session etc.These can be defined in at client side and server side state management.
What is AppDomain
An AppDomain can be defined as light weight process and is used for security isolation and availability. AppDomain is hosted on some process and a Process can host multiple AppDomains. So one AppDomain can go down/restarts without affecting other AppDomains in the same process.
An AppDomain can be defined as light weight process and is used for security isolation and availability. AppDomain is hosted on some process and a Process can host multiple AppDomains. So one AppDomain can go down/restarts without affecting other AppDomains in the same process.
Role of AppDomain in ASP.NET:
AppDomain plays a key role in asp.net. When ASP.NET receives first request, the Application manager creates an application domain for it, Application domain are very important because they provide the isolation amongst various applications on the web server and every application domain is loaded and unloaded separately and in application domain an instance of class HostingEnvironment is created which provides access to information about all application resources.
AppDomain plays a key role in asp.net. When ASP.NET receives first request, the Application manager creates an application domain for it, Application domain are very important because they provide the isolation amongst various applications on the web server and every application domain is loaded and unloaded separately and in application domain an instance of class HostingEnvironment is created which provides access to information about all application resources.
So Now AppDomain is responsible all the server side side management, means all the data session(InProc mode) Application Objects/Variable Cache all resides in AppDomain itself. If AppDomain goes down, all the data at web server will be wiped off. Let’s have a View
Web Farm is used in Highly available application and which have a lot of users that cannot be served by single server. Then we use Web Farm. They provides better performance and also easily scalable. It means we’ll be having multiple web servers behind a Network Load Balancer (NLB). So now whenever a request comes, it first goes to the load balancer, it checks all the available web servers and which has comparatively less requests to serve, passes the requests to that web server.
Most of the large applications are deployed in Web Farm scenario. A Single server might not able to handle millions of requests in a day and we provide a virtual IP to the Load Balancer and the URL is mapped to Load Balancer, and load balancer takes a decision to pass the request to a specific web server.
So in this scenario, the Session mode InProc does not work. We require to use OutProc mode, because might be, at first request is served by some server1 and store some session data, but later it another request Load balancer finds that server1 is busy handling another requests and it can pass this to another server, which obviously does not have session data and it can result in a bizarre.
In OutProc mode Session data is not stored in the AppDomain of web server. In this we store the data some another server. We’ll discuss it in brief later.
Affinity
There is a setting known as affinity parameter setting, can be set so that Load balancer directs all the requests from one Client IP address to the same machine. This allows us to use Session (InProc mode), Application data and Cache in Web Farm scenario seamlessly. Means the application would work like it is deployed on single server only. But it has few limitation like below.
There is a setting known as affinity parameter setting, can be set so that Load balancer directs all the requests from one Client IP address to the same machine. This allows us to use Session (InProc mode), Application data and Cache in Web Farm scenario seamlessly. Means the application would work like it is deployed on single server only. But it has few limitation like below.
- If the server serving request, goes down in between, all the server data would be lost.
- This limits the use of Web Farm as Load balancer would be confined to redirect to the requests for the same Client machines to a single Web server only.
What is Web Garden:
When we deploy our application on IIS(6 and above). We assign an application pool to out application. Application pool is used for isolation purpose from another application deployed on the same web server. So an application pool is having on worker process(w3wp.exe) normally. An AppDomain is created over this Worker process, that handles/serves the requests send by the client machines. All the server data(Session, Cache , Static Variables, Application variables) is stored in AppDomain boundary. But we can have multiple worker process on the same application pool for performance benefits. It allows better handling the web request sent by the Client machines. But these worker process does not share the memory And a new AppDomain is created for the same Application and each AppDomain has its own copy of data. Means if some session is stored in one AppDoain’s memory and the next request is handled by another web server it won’t be having the session data.
When we deploy our application on IIS(6 and above). We assign an application pool to out application. Application pool is used for isolation purpose from another application deployed on the same web server. So an application pool is having on worker process(w3wp.exe) normally. An AppDomain is created over this Worker process, that handles/serves the requests send by the client machines. All the server data(Session, Cache , Static Variables, Application variables) is stored in AppDomain boundary. But we can have multiple worker process on the same application pool for performance benefits. It allows better handling the web request sent by the Client machines. But these worker process does not share the memory And a new AppDomain is created for the same Application and each AppDomain has its own copy of data. Means if some session is stored in one AppDoain’s memory and the next request is handled by another web server it won’t be having the session data.
Affinity:
Now the question: Do we have some affinity settings in WebGarden scenario? yes
There is a hardcoded client connection affinity to a worker process instance. So for a given client TCP connection all the HTTP requests will be handled by the same instance of the worker process.
So as we all have seen that in case of setting Affinity parameter, we can host our Application in WebFarm/WebGarden scenario without worrying about, How web server data is going to be stored and managed.It will be working seamlessly as your application is hosted on single server only.
But as we discussed the limitation the affinity parameter, It is not advisable to set the affinity parameter.
Something more about Session Management:
Something more about Session Management:
Let’s discuss Session a bit
As we know, these are stored on Web server. First let’s have a quick Idea about How Session is stored .
There are two modes for storing session.
InProcOutProc
InProc:In this mode, Session values are stored AppDomain on webserver where application is running itself. As this is stored in server memory its highly efficient in performance point of view. But this is not very scalable and robust, because as the users at the application increasing, you application may face some tough time while processing multiple requests and it can go down. But obviously, you would not want that your website goes down. And also for highly available websites, this does not work.
OutProc:Here the data in session is not stored in the AppDomain on the webserver memory. And whenever your data goes out from webserver memory, you need to serialize and need deserialize again before using this. Here this is one performance overhead. Here the session stored on mainly in three ways:
StateServer: In this, Session information in state server that is a process, known as ASP.NET state service, that is separate from the ASP.NET worker process. But this is a single point of failure. But if this service/box goes down, your application will stop working abruptly.
Sql Server: Here, we store the session in Sql Server..NET provides some default scripts that can be used to install at SQL and it gets ready to use to store session data Also there we can have cluster, by maintaining the Session on several machines. So if one goes down, The user requests can be served from other box.
Custom Aproach: ASP.NET provides us the flexibility to write our own custom provider for maintaining and storing Session data. This provides us to store the session data where and how as we want.
Now we are going to discuss Cache management.
Should we not use the Application state in case of WebFarm/WebGarden scenarios?
We have lot discussed about the Session in these scenarios. But I found people having less Idea other states like Application and others like Cache.
Lets discuss Cache
How to handle Cache in Web Farm/Web Garden scenario:
How to handle Cache in Web Farm/Web Garden scenario:
To start with, you must have some basic Idea about Cache management in ASP.NET.
How we can handle Cache which resides in AppDomain in web farm or web garden scenario
The best way to don’t use Cache in Web Farm and web Garden Scenario.
Frankly speaking. It depends on the requirements, the kind of data you are going to have in your Cache.
If you have really static data, like country names, so these is static data and is not going to be changed every now and again. So in this case it does not matter, whether is in web farm/web garden scenario, if the data would not be available in the AppDomain, it will get loaded from the database. And obviously its not going to changed once loaded so no worries in case of Web Farm/Web Garden.
So here I will be discussing case by case with the specific scenario
Scenario 1:
You have some data in file system. Say you have lots of data in our config file, which is frequently used. So here reading again and again from the config file would not be good approach. Better have it in Cache and retrieve it from there whenever required.
You have some data in file system. Say you have lots of data in our config file, which is frequently used. So here reading again and again from the config file would not be good approach. Better have it in Cache and retrieve it from there whenever required.
Approach: This is very basic scenario: you can load the data initially, when there is no data in Cache and set the dependency on the file. Means whenever there is any change in file, the cache will be invalidated and will get updated and this will be valid for all the AppDomain across web farm/web garden.
Scenario 2:
One might have the scenario, that there is some master data, that is used by entire application frequently. So in this scenario, it might not be a good approach to get the data the from database every time you need it. So better to have it in Cache. One more thing, This master can be updated by Admin with a new Interface.
Aprroach:
I think this is very basic requirement and best candidate for using Cache. As the data is almost static and will be updated very infrequently. So now, There is some master data. That we can load first time when it is not in cache and pick from it whenever required. As I discussed in the scenario, Their might be some admin interface which is only able to enter the master and update it in database. At this point, one need to update the Cache for all the AppDomain on all the web servers. So here in webfarm scenario, you data is coming from database, so you can set the dependency on database so that as soon as the data gets updated in your database the cache will be invalidated on all the web servers and get reloaded with updated data from database. So this is a common scenario and one does not need to worry about Data syncing
One might have the scenario, that there is some master data, that is used by entire application frequently. So in this scenario, it might not be a good approach to get the data the from database every time you need it. So better to have it in Cache. One more thing, This master can be updated by Admin with a new Interface.
Aprroach:
I think this is very basic requirement and best candidate for using Cache. As the data is almost static and will be updated very infrequently. So now, There is some master data. That we can load first time when it is not in cache and pick from it whenever required. As I discussed in the scenario, Their might be some admin interface which is only able to enter the master and update it in database. At this point, one need to update the Cache for all the AppDomain on all the web servers. So here in webfarm scenario, you data is coming from database, so you can set the dependency on database so that as soon as the data gets updated in your database the cache will be invalidated on all the web servers and get reloaded with updated data from database. So this is a common scenario and one does not need to worry about Data syncing
Scenario 3:
This is common scenario. Where we store some data in Cache at the server. And it can get updated at any time. So How to handle it in WebFarm and Web Garden scenario.
Note: Here I am discussing only few approaches to handle Cache in web farm/web garden scenario. There can be many more ways to handle this.
Approach 1:
Note: Here I am discussing only few approaches to handle Cache in web farm/web garden scenario. There can be many more ways to handle this.
Approach 1:
Here the basic approach is , as soon as , the data in any of the cache gets updated, it will invoke a web service call to all the web servers which will update the cache in all the associated web servers behind the Load Balancer. So here we can have a table in database, which will have the IP of the webserver connected in web farm (These IP will the direct IP of the web servers not the load balancer virtual IP). Let’s see it in steps.
- There will a table in database having the entry of the IPs of all the webservers under the load balancer.
- There will be the webservice, that will get the ips of all the webservers and update the cache one by one.
- The webservice will be invoked by any of the webserver behind the load balancer on which cache will get updated.
- Here it is also to to add a new webserver under load balancer to cater the new needs. Just add that the table which have all the IPs of webserver.
Approach 2:
In this, your cache not on the web server but you can store it on some another server. So every web server is going to connect this machine to get the cached data. Now you will be asking if the cache is stored on some another box, what will the performance benefit we’ll get. So I would suggest you to have a remoting (TCP) connection to that caching server and it is so fast to get the data from there, that there would not be any much difference in having the data at web servers memory or at another cache server.
i think this is a very easy way to understand to state management along with web Farm and web Garden.....
thnx for reading this:
krishan kayat.








Comments
Post a Comment